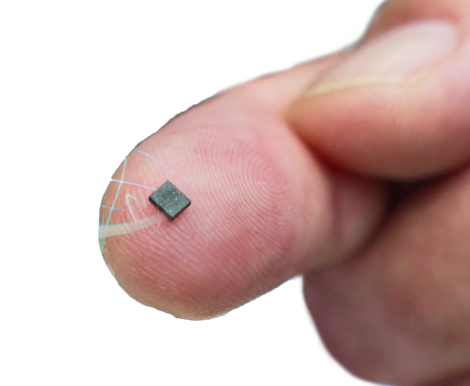
- All ML analysis is performed within the low-power sensor
- Optimized for enhanced battery efficiency, minimizing power consumption
- Seamless integration into ultra-low power smart sensors
Neuton is a no-code Tiny AutoML platform empowered by a patented Neural Network Framework under the hood. Offering a highly automated and transparent pipeline, Neuton doesn't require a lot of actions from the user's side. It helps to automatically build extremely compact and accurate models without additional compression and natively embed them into 8, 16, and 32-bit MCUs!
Free for DevelopersWith this solution, you can use a smart ring to control your TV through various gestures.
Our solution can detect and log how many times a user has washed their hands.
This ready-made solution allows for various gestures to interact with smartwatches and other wearables.
This solution can recognize seven different events that may occur during the package delivery process.
The solution is capable to recognize daily human activities directly on the ultra-low power ISPU sensor.
The solution can identify which specific area of your oral cavity needs cleaning and how effectively it is being cleaned.
This solution of <4 kb in total footprint can remotely control your media system or presentation slides through gestures.
 Reproduce it
Reproduce it
The solution is highly efficient and has a small footprint. It can recognize complex human activity and can be easily replicated on your device.
Neuton is based on a unique patented machine learning algorithm that forgoes error backpropagation and stochastic gradient descent, growing the network structure neuron by neuron. This helps to build neural networks without compromising between accuraсy and size:


Ever thought about how water enters the central heating pipes? The secret is the proper operation of water pumps. Learn how to use RSL10 sensors and Neuton to run models for timely pump maintenance.
How to quickly develop TinyML models to recognize custom, user-defined drawn gestures on touch interfaces? Check out the project inspired by a gesture recognition feature on a simple smartphone.
Electricity permeates the entire infrastructure of modern cities, so it's really important to monitor and prevent overloads. Explore how to predict electrical grid stability with Neuton and Particle IoT.
| Total Footprint (kb) | TFLM | Neuton | Neuton Advantages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flash | TinyML framework (model + inference engine + DSP) | 79.96 | 5.42 |
14 times
smaller
|
| Device drivers and business logic | 93.47 | 93.47 | ||
| SRAM | TinyML framework (model + inference engine + DSP) | 18.2 | 1.72 |
10 times
smaller
|
| Device drivers and business logic | 45.69 | 45.69 | ||
| Inference time (us) | 55 262 | 1 640 |
33 times
faster
|
|
| Holdout validation Accuracy | 0.93 | 0.94 |
0,7%
higher accuracy
|
|
| Total Footprint (kb) | TFLM | Neuton |
|---|---|---|
| Flash | ||
| TinyML framework (model + inference engine + DSP) | 79.96 | 5.42 |
| Device drivers and business logic | 93.47 | 93.47 |
| Neuton Advantages |
14 times
smaller
|
|
| SRAM | ||
| TinyML framework (model + inference engine + DSP) | 18.2 | 1.72 |
| Device drivers and business logic | 45.69 | 45.69 |
| Neuton Advantages |
10 times
smaller
|
|
| Inference time (ms) | TFLM | Neuton |
| 55 262 | 1 640 | |
| Neuton Advantages |
33 times
faster
|
|
| Holdout validation Accuracy | TFLM | Neuton |
| 0.93 | 0.94 | |
| Neuton Advantages |
0,7%
higher occuracy
|
|
| Case | Holdout Accuracy | Inference Time, us | SRAM, kB | FLASH, kB | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuton | PME* | More accurate | Neuton | PME* | Times faster | Neuton | PME* | Times smaller | Neuton | PME* | Times smaller | |
| Gearbox Fault Diagnosis | 0.84 | 0.74 | 12% | 56 776 | 84 080 | 1.5 | 3.54 | 4.95 | 1.3 | 9.64 | 11.15 | 1.1 |
| Air-Writing Digits Recognition | 0.93 | 0.82 | 12% | 18 172 | 52 000 | 2.9 | 2.57 | 4.92 | 1.9 | 8.91 | 9.79 | 1.1 |
| Arrhythmia Diagnostic binary | 0.93 | 0.72 | 23% | 5 212 | 106 220 | 20 | 0.98 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 2.59 | 8.61 | 3.3 |
| Arrhythmia Diagnostic multi | 0.96 | 0.77 | 20% | 14 232 | N/A | N/A | 2.58 | 9.31 | 3.6 | 6.24 | 16.95 | 2.7 |

Experience the potential of In-sensor AI at the STMicroelectronics booth 4A-148 at Embedded World 24

We were delighted to present our joint In-Sensor AI project with STMicroelectronics at the Mobile World Congress 2024.
![Arm Tech Talk 2024: TinyML in Assistive Technology [Webinar]](/uploads/posts/2024-04/2-9.jpg)
Watch the Arm Tech Talk focused on TinyML in assistive technology and discover the simple process of creating such devices using the Neuton.AI platform.
